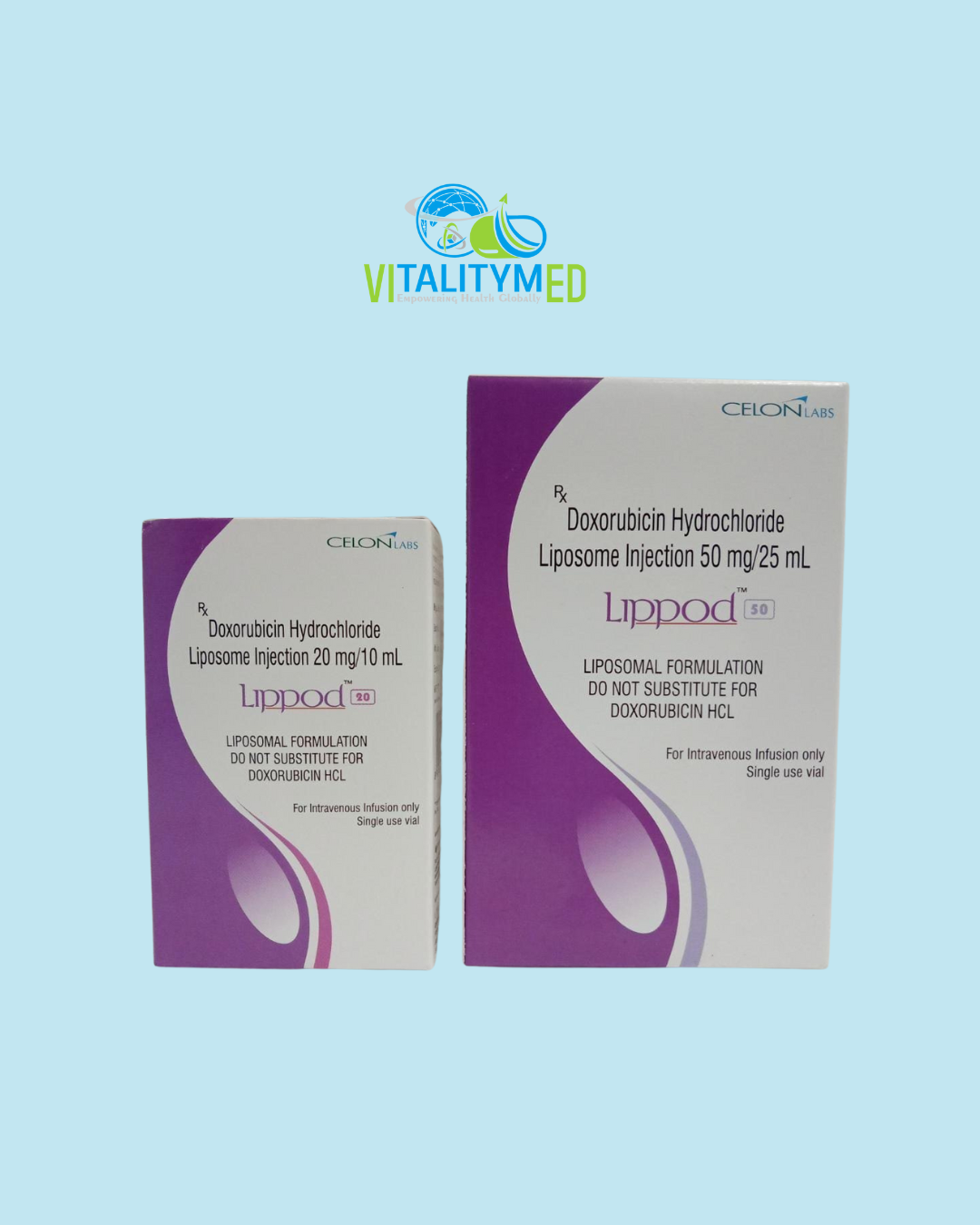
Lippod contains Doxorubicin Hydrochloride, an anthracycline antibiotic used as a powerful chemotherapeutic agent, formulated here as a liposomal injection.
-
Available as 20 mg/10 ml and 50 mg/25 ml vials, this liposomal form encapsulates doxorubicin in tiny lipid vesicles, improving delivery directly to tumour tissues while reducing distribution to healthy tissues.
-
This innovation helps limit some of the severe toxicities seen with conventional doxorubicin, especially heart-related side effects, making it a valuable option in cancer therapy.
Mechanism of Action
Doxorubicin, whether liposomal or conventional, fights cancer through multiple mechanisms:
-
DNA intercalation: It slips between DNA base pairs, disrupting the double helix structure and blocking DNA replication.
-
Inhibition of topoisomerase II: Prevents DNA from unwinding and resealing, leading to breaks in DNA strands.
-
Generation of free radicals: Adds to DNA and cell membrane damage.
The liposomal formulation:
-
Allows the drug to circulate longer in the bloodstream.
-
Preferentially accumulates in tumour tissues due to their leaky blood vessels (enhanced permeability and retention effect).
-
Reduces exposure of healthy tissues (like heart muscle), thereby lowering cardiotoxic risks.
Uses / Indications
Lippod is used in the treatment of various cancers, including:
-
Metastatic breast cancer, especially in patients who may be at increased risk of heart damage with conventional doxorubicin.
-
Ovarian cancer, particularly platinum-refractory or relapsed disease.
-
Multiple myeloma, in combination with other agents like bortezomib.
-
AIDS-related Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS).
Its usage is typically under specialised oncology protocols, and doses are adjusted based on body surface area and individual tolerance.
Adverse Effects
Though liposomal doxorubicin reduces some risks compared to standard doxorubicin, it still carries important side effects requiring careful monitoring.
Common side effects include:
-
Bone marrow suppression: low white cells, platelets, or red cells—necessitating regular blood counts.
-
Hand-foot syndrome (palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia): redness, swelling, or peeling of palms and soles.
-
Mouth sores (stomatitis) and gastrointestinal issues like nausea or diarrhoea.
-
Fatigue and mild hair thinning.
Less common but serious effects:
-
Heart toxicity (cardiomyopathy) — less frequent than with conventional doxorubicin but still monitored by periodic echocardiograms.
-
Severe infusion reactions — including flushing, shortness of breath, or chest tightness during administration.
-
-