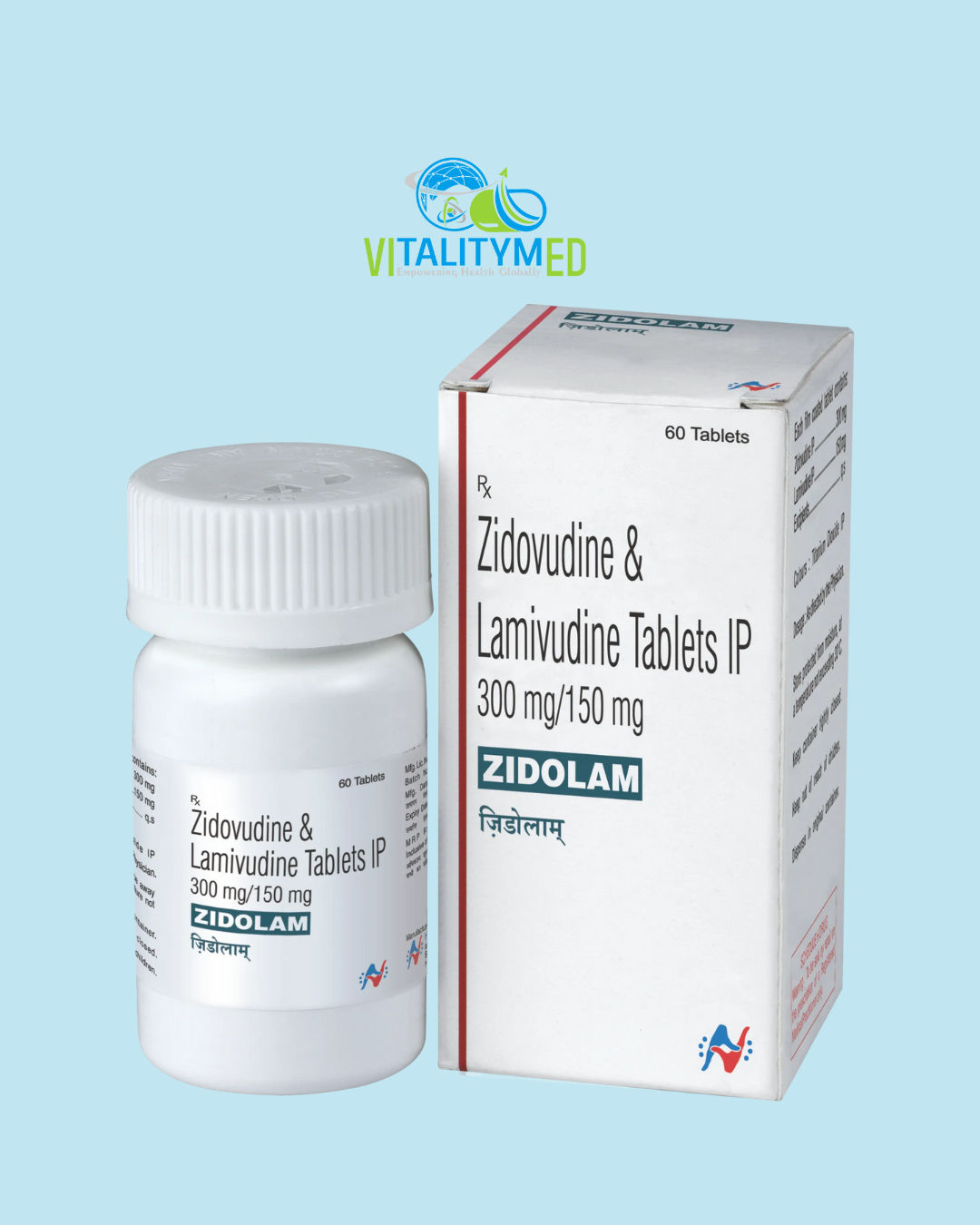
Zidolam is a combination antiretroviral medicine used in the treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection. It contains two active ingredients: zidovudine and lamivudine, both of which belong to a class of drugs called nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Zidolam is used as part of a combination therapy to manage HIV infection, reduce viral load, and help restore and maintain immune function.
Uses:
Zidolam is used for:
-
The treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and children as part of combination antiretroviral therapy.
-
It is often prescribed in combination with other antiretroviral medicines to improve effectiveness and reduce the risk of drug resistance.
Mechanism of Action:
Zidolam works by interfering with the ability of the HIV virus to replicate in the body:
-
Zidovudine is one of the earliest antiretroviral drugs and mimics a natural building block of DNA. It gets incorporated into the viral DNA chain during replication, leading to early termination and preventing further virus production.
-
Lamivudine works similarly by blocking the reverse transcriptase enzyme that HIV uses to convert its RNA into DNA, a key step in its replication cycle.
Adverse Effects:
Zidolam is generally effective, but some individuals may experience side effects. Common ones include:
-
Headache
-
Nausea
-
Tiredness
-
Muscle pain
-
Digestive discomfort